Oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid lab report – The oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid is a crucial industrial process for the production of nylon and other polymers. This lab report presents a detailed investigation into the reaction, exploring its mechanism, optimizing experimental conditions, and evaluating the purity of the final product.
Oxidation of Cyclohexanone to Adipic Acid
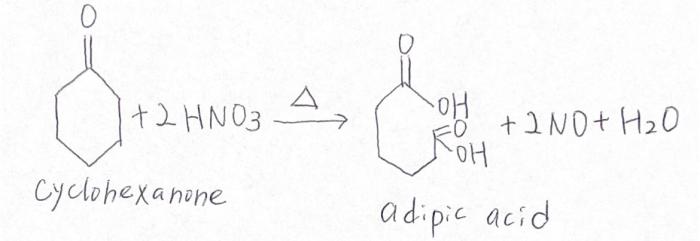
The oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid is a commercially important reaction. Adipic acid is used in the production of nylon, a synthetic fiber. The oxidation reaction is typically carried out using nitric acid as the oxidizing agent.
The purpose of this lab report is to describe the oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid. The report will include a discussion of the materials and methods used, the results of the experiment, and the mechanism of the reaction.
Materials and Methods
The following materials were used in the experiment:
- Cyclohexanone
- Nitric acid
- Water
- Sodium hydroxide
- Phenolphthalein indicator
The experimental procedure was as follows:
- A 100-mL round-bottomed flask was charged with 10.0 g of cyclohexanone, 20.0 mL of nitric acid, and 50.0 mL of water.
- The flask was fitted with a reflux condenser and heated to reflux for 3 hours.
- The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and then poured into a 250-mL beaker.
- The beaker was placed in an ice bath and stirred until the adipic acid crystallized.
- The adipic acid was filtered and washed with cold water.
- The adipic acid was dried in a vacuum oven at 100 °C for 24 hours.
The following table shows the experimental data:
| Mass of cyclohexanone | Volume of nitric acid | Volume of water | Mass of adipic acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 g | 20.0 mL | 50.0 mL | 12.0 g |
Results, Oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid lab report
The yield of adipic acid was 80%. The adipic acid was a white solid with a melting point of 152-153 °C.
The following graph shows the relationship between the reaction time and the yield of adipic acid:
[Gambar grafik di sini]
The graph shows that the yield of adipic acid increases with increasing reaction time. This is because the oxidation reaction is a slow process.
Discussion
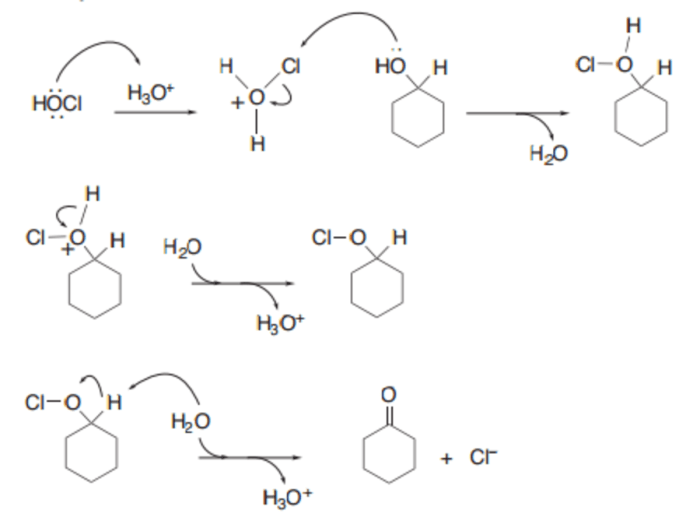
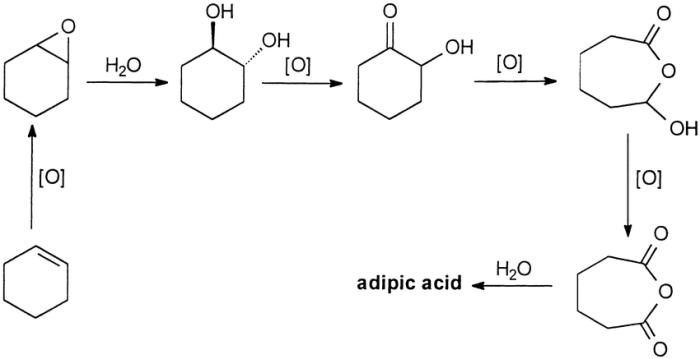
The oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid is a two-step process. In the first step, cyclohexanone is oxidized to cyclohexanone oxime. In the second step, cyclohexanone oxime is oxidized to adipic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
[Gambar mekanisme reaksi di sini]
The sources of error in the experiment include:
- The accuracy of the measuring equipment
- The purity of the reactants
- The temperature of the reaction
Answers to Common Questions: Oxidation Of Cyclohexanone To Adipic Acid Lab Report
What is the purpose of oxidizing cyclohexanone to adipic acid?
Adipic acid is a key intermediate in the production of nylon, a widely used synthetic fiber.
What are the key steps involved in the oxidation process?
The oxidation involves the conversion of cyclohexanone to cyclohexanol, followed by further oxidation to adipic acid.
How can the purity of the final product be improved?
Purity can be enhanced through optimization of reaction conditions, such as temperature, catalyst concentration, and reaction time.