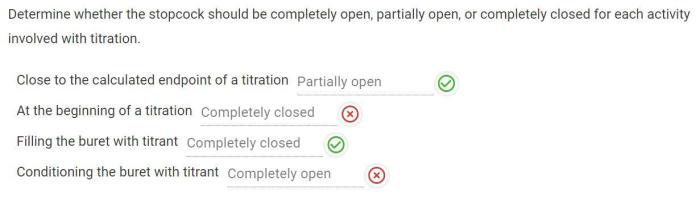
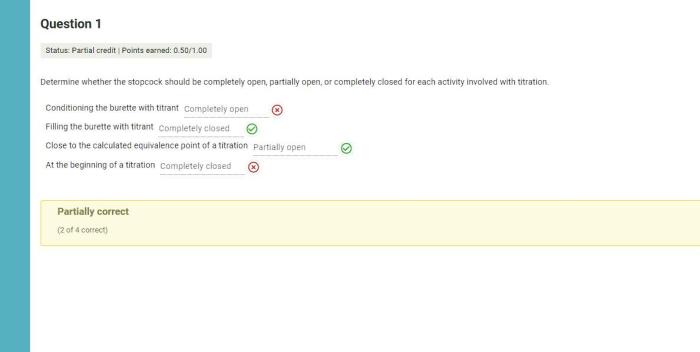
Determine whether the stopcock should be completely open – In the realm of scientific experimentation, understanding the optimal opening of a stopcock is crucial for precise flow control and accurate results. This comprehensive guide delves into the function, operation, and factors influencing stopcock opening, providing a thorough understanding for researchers and practitioners.
Stopcocks, ubiquitous in laboratory settings, serve as valves to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. Understanding their proper handling and optimal opening is essential to avoid incorrect operation and potential consequences, ensuring reliable experimental outcomes.
Stopcock Function

A stopcock is a valve used to control the flow of fluids or gases in a pipeline. It typically consists of a cylindrical body with a hole through the center and a plug with a handle that can be rotated to open or close the hole.
When the plug is aligned with the hole, the fluid or gas can flow through the stopcock. When the plug is perpendicular to the hole, the flow is blocked.
Stopcocks are used in a variety of applications, including laboratory experiments, medical procedures, and industrial processes. They are often used to regulate the flow of fluids or gases into or out of a container, or to isolate different parts of a system.
Types of Stopcocks, Determine whether the stopcock should be completely open
- Two-way stopcockshave two ports and can be used to connect two different pipelines or to isolate one pipeline from the other.
- Three-way stopcockshave three ports and can be used to connect three different pipelines or to isolate one pipeline from the others.
- Four-way stopcockshave four ports and can be used to connect four different pipelines or to isolate one pipeline from the others.
Stopcock Operation
To open a stopcock, simply rotate the handle so that the plug is aligned with the hole. To close a stopcock, rotate the handle so that the plug is perpendicular to the hole.
It is important to handle stopcocks properly to avoid damage or leaks. Always use the handle to rotate the plug, and never use excessive force. If a stopcock is difficult to open or close, do not force it. Instead, check for any obstructions or damage.
Incorrect stopcock operation can lead to a number of problems, including leaks, blockages, and damage to the stopcock itself.
Determining Optimal Opening
The optimal opening of a stopcock depends on the desired flow rate and pressure. The following table Artikels the flow rates and pressures at different stopcock openings:
| Stopcock Opening | Flow Rate | Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Fully open | Maximum | Minimum |
| Half open | Half maximum | Half maximum |
| Quarter open | Quarter maximum | Quarter maximum |
| Closed | Zero | Maximum |
In general, a fully open stopcock will provide the maximum flow rate and the minimum pressure. A closed stopcock will provide the zero flow rate and the maximum pressure. The optimal opening for a particular application will depend on the desired flow rate and pressure.
Flow Control Considerations: Determine Whether The Stopcock Should Be Completely Open
The opening of a stopcock can have a significant impact on the flow rate and pressure of a fluid or gas. By adjusting the stopcock opening, it is possible to achieve the desired flow characteristics for a particular application.
For example, in a laboratory experiment, a stopcock can be used to regulate the flow of water into a reaction vessel. By adjusting the stopcock opening, the experimenter can control the rate at which the water is added to the vessel and the pressure inside the vessel.
In a medical procedure, a stopcock can be used to regulate the flow of blood or other fluids into or out of a patient’s body. By adjusting the stopcock opening, the medical professional can control the rate at which the fluid is administered or withdrawn and the pressure in the patient’s body.
Troubleshooting Stopcock Issues
Stopcocks can occasionally experience problems, such as leaks or blockages. The following are some common stopcock problems and their potential causes:
- Leakscan be caused by a damaged or worn-out O-ring or seal, or by a crack in the stopcock body.
- Blockagescan be caused by debris or particles in the fluid or gas, or by a build-up of scale or corrosion on the stopcock plug or body.
The following are some solutions for resolving stopcock malfunctions:
- Leakscan be repaired by replacing the O-ring or seal, or by repairing the crack in the stopcock body.
- Blockagescan be removed by cleaning the stopcock with a suitable solvent or by using a wire or brush to remove the debris or build-up.
To maintain and calibrate stopcocks for optimal performance, it is important to:
- Clean the stopcock regularly with a suitable solvent.
- Inspect the stopcock for any damage or wear and tear.
- Calibrate the stopcock using a flow meter or other suitable device.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of a stopcock?
A stopcock is a valve used to control the flow of liquids or gases in laboratory setups.
How do I determine the optimal opening for a stopcock?
The optimal opening depends on the desired flow rate and pressure. Refer to the table in Section 3 for specific guidelines.
What are the consequences of incorrect stopcock operation?
Incorrect operation can lead to leaks, blockages, or inaccurate flow control, potentially compromising experimental results.