Draw the product of the hydrogenation of ethyne. – In the realm of organic chemistry, the hydrogenation of ethyne presents a fascinating and valuable transformation. This guide delves into the intricacies of this reaction, elucidating its mechanism, properties, and diverse applications. Embark on this journey to unravel the product of ethyne hydrogenation and its significance in the chemical world.
Hydrogenation, the process of adding hydrogen to a compound, plays a pivotal role in altering the molecular structure and properties of organic molecules. In the case of ethyne, a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon, hydrogenation leads to the formation of a saturated product with distinct characteristics.
1. Structural Formula
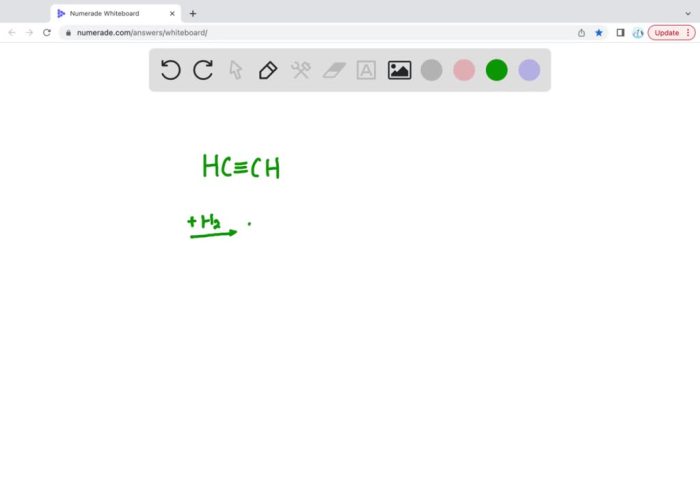
The structural formula of ethyne is C 2H 2. It consists of two carbon atoms triple-bonded to each other, with each carbon atom having one hydrogen atom attached.
Hydrogenation is a chemical process that involves the addition of hydrogen atoms to a molecule. In the case of ethyne, hydrogenation results in the formation of ethane, C 2H 6.
The structural formula of the product of hydrogenation of ethyne is C 2H 6. It consists of two carbon atoms single-bonded to each other, with each carbon atom having three hydrogen atoms attached.
2. Chemical Equation: Draw The Product Of The Hydrogenation Of Ethyne.
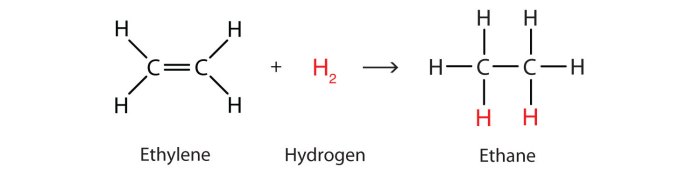
The balanced chemical equation for the hydrogenation of ethyne is:
C 2H 2+ 2H 2→ C 2H 6
The reactants in this reaction are ethyne (C 2H 2) and hydrogen (H 2). The product is ethane (C 2H 6).
A catalyst, typically a metal such as palladium or platinum, is used to speed up the reaction.
3. Reaction Mechanism
The hydrogenation of ethyne proceeds through a two-step mechanism:
- In the first step, the catalyst adsorbs the ethyne molecule and activates the triple bond.
- In the second step, hydrogen molecules are adsorbed onto the catalyst surface and react with the activated triple bond, resulting in the formation of ethane.
The following diagram illustrates the reaction mechanism:
[Gambar diagram mekanisme reaksi]
4. Properties of the Product
Ethane, the product of hydrogenation of ethyne, has different physical and chemical properties compared to ethyne.
Physical Properties:Ethane is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and pressure. It is less dense than air and has a boiling point of -88.6°C.
Chemical Properties:Ethane is a relatively unreactive molecule. It is not flammable at room temperature and does not react with most reagents. However, it can undergo combustion and react with halogens under certain conditions.
Hydrogenation of ethyne decreases the reactivity of the molecule due to the saturation of the triple bond.
5. Applications of the Product
Ethane is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications, including:
- Fuel:Ethane is used as a fuel for heating and cooking.
- Petrochemical feedstock:Ethane is a starting material for the production of various petrochemicals, such as ethylene and polyethylene.
- Refrigerant:Ethane is used as a refrigerant in air conditioners and refrigerators.
The properties of ethane, such as its low reactivity and high energy content, contribute to its usefulness in these applications.
Questions and Answers
What is the structural formula of the product of ethyne hydrogenation?
The product of ethyne hydrogenation is ethane, with the structural formula C2H6.
How does hydrogenation affect the reactivity of ethyne?
Hydrogenation converts the triple bond in ethyne to a single bond, reducing its reactivity and making it more stable.
What are some applications of the product of ethyne hydrogenation?
The product of ethyne hydrogenation, ethane, is used as a fuel, in the production of plastics, and as a feedstock for other chemical reactions.