Gse geometry unit 4 circles and arcs answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey into the captivating world of geometry as we delve into GSE Geometry Unit 4: Circles and Arcs. This comprehensive guide unlocks the intricacies of these fundamental shapes, providing a solid foundation for understanding their properties, relationships, and practical applications.
Through engaging explanations, real-world examples, and a wealth of problem-solving strategies, we will unravel the mysteries of circles and arcs, empowering you to conquer any geometry challenge that comes your way.
Circles and Arcs: Concepts and Applications
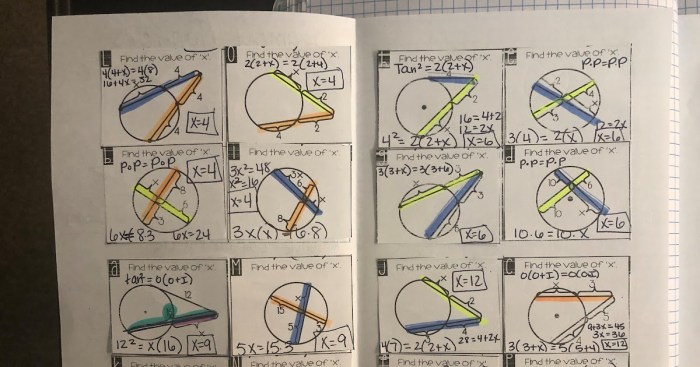
Circles and arcs are fundamental geometric shapes that play a crucial role in various fields. This article delves into the definitions, properties, relationships, and applications of circles and arcs, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential concepts.
Definitions and Concepts
A circle is a closed, two-dimensional shape defined by a fixed distance from a central point called the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is known as the radius.
An arc is a portion of a circle defined by two endpoints and the points on the circle between them. The endpoints of an arc are called its endpoints, and the distance along the circle between the endpoints is called its arc length.
Properties of Circles and Arcs
Circles possess several important properties:
- The radius of a circle is equal to half of its diameter.
- The circumference of a circle is equal to 2πr, where r is the radius.
- The area of a circle is equal to πr 2, where r is the radius.
Arcs also have specific properties:
- The arc length of an arc is proportional to the central angle that it subtends.
- The area of a sector of a circle, which is the region bounded by an arc and two radii, is equal to (θ/360)πr 2, where θ is the central angle in degrees and r is the radius of the circle.
Relationships between Circles and Arcs, Gse geometry unit 4 circles and arcs answer key
Circles and arcs are closely related. The radius of a circle determines the length of an arc subtended by a given central angle.
The relationship between the arc length, central angle, and radius is given by the formula: Arc length = (θ/360)2πr, where θ is the central angle in degrees, r is the radius of the circle, and π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14.
Applications of Circles and Arcs
Circles and arcs have numerous applications in engineering, architecture, and design:
- In engineering, circles and arcs are used to design gears, pulleys, and other mechanical components.
- In architecture, circles and arcs are used to create domes, arches, and other curved structures.
- In design, circles and arcs are used to create logos, symbols, and other visual elements.
Solving Problems Involving Circles and Arcs
To solve problems involving circles and arcs, it is essential to understand the formulas and concepts discussed in this article. The following table summarizes key formulas:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Radius = Diameter / 2 | The radius of a circle is half of its diameter. |
| Circumference = 2πr | The circumference of a circle is 2π times its radius. |
| Area of a circle = πr2 | The area of a circle is π times its radius squared. |
| Arc length = (θ/360)2πr | The arc length of an arc is (θ/360) times 2π times the radius of the circle, where θ is the central angle in degrees. |
| Area of a sector = (θ/360)πr2 | The area of a sector of a circle is (θ/360) times π times the radius of the circle squared, where θ is the central angle in degrees. |
To solve problems, follow these steps:
- Identify the given information and what is being asked.
- Choose the appropriate formula.
- Substitute the given values into the formula.
- Solve for the unknown.
FAQs: Gse Geometry Unit 4 Circles And Arcs Answer Key
What is the formula for the circumference of a circle?
Circumference = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
How do you find the area of a sector of a circle?
Area of sector = (θ/360) × πr², where θ is the central angle of the sector and r is the radius of the circle.
What is the relationship between the radius of a circle and the length of an arc?
Arc length = (θ/360) × 2πr, where θ is the central angle of the arc and r is the radius of the circle.