Welcome to the comprehensive guide to mitosis and meiosis test answer key, where we unravel the intricate processes of cell division. From the fundamental principles of mitosis to the complexities of meiosis, this resource provides a thorough understanding of these vital biological mechanisms.
Delve into the fascinating world of cell biology as we explore the stages, significance, and distinctions between mitosis and meiosis. Gain insights into their crucial roles in cell growth, development, and reproduction.
Mitosis: Mitosis And Meiosis Test Answer Key
Mitosis is a fundamental process in cell biology, ensuring the accurate division of genetic material during cell reproduction. It is a continuous process, but for descriptive purposes, it is divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Each stage plays a crucial role in the faithful segregation of chromosomes, ensuring the genetic stability of daughter cells.
Stages of Mitosis
- Prophase:Chromosomes become visible, and the nuclear envelope begins to disintegrate. Spindle fibers form to capture the chromosomes and align them at the center of the cell.
- Metaphase:Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of genetic material.
- Anaphase:Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell, driven by the shortening of spindle fibers.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes, and the spindle fibers disappear. Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, follows, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
Role of Mitosis in Cell Division
Mitosis is essential for cell growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction. It ensures that each daughter cell inherits an identical copy of the genetic material, maintaining the genetic integrity of the organism. Mitosis also plays a role in the development of specialized cell types during embryonic development and in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis throughout an organism’s life.
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
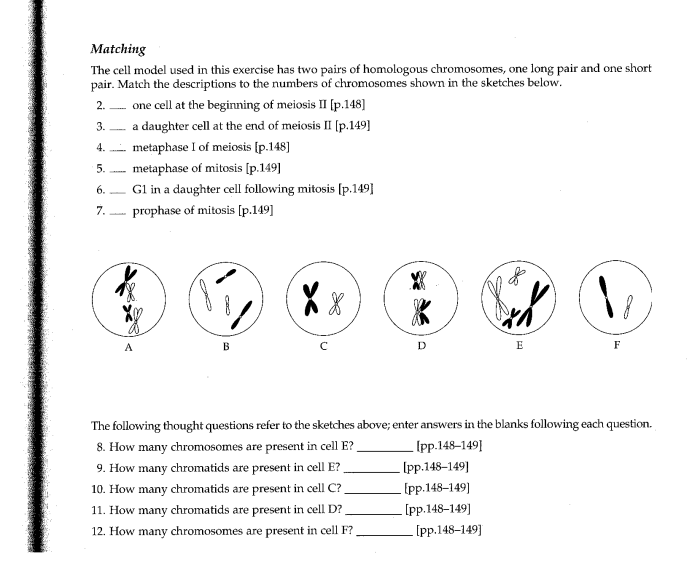
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that occur in eukaryotic organisms. Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is the process by which a single cell divides into four haploid daughter cells.
Both mitosis and meiosis are essential for the growth and development of organisms.
There are several key similarities between mitosis and meiosis. Both processes involve the division of a cell into two or more daughter cells, and both processes involve the duplication of chromosomes prior to division. However, there are also several key differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Similarities between Mitosis and Meiosis, Mitosis and meiosis test answer key
- Both mitosis and meiosis involve the division of a cell into two or more daughter cells.
- Both mitosis and meiosis involve the duplication of chromosomes prior to division.
- Both mitosis and meiosis occur in eukaryotic organisms.
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells.
- Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, while meiosis occurs in germ cells.
- Mitosis is used for growth and development, while meiosis is used for reproduction.
The following table summarizes the key differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Type of daughter cells | Identical | Haploid |
| Location | Somatic cells | Germ cells |
| Purpose | Growth and development | Reproduction |
Test Answer Key
This answer key provides comprehensive explanations for each question in the mitosis and meiosis test. It is organized into sections covering both mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis
Question 1: What is the primary function of mitosis?
Answer: Mitosis is responsible for cell growth and repair, ensuring that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material from the parent cell.
Question 2: Describe the four phases of mitosis in order.
Answer: The four phases of mitosis are: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Question 3: What is the role of the spindle fibers during mitosis?
Answer: Spindle fibers are responsible for separating the chromosomes during anaphase, ensuring that each new cell receives an equal number of chromosomes.
Meiosis
Question 1: What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Answer: Meiosis produces four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while mitosis produces two diploid cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Question 2: Describe the two divisions of meiosis in order.
Answer: The two divisions of meiosis are meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I reduces the chromosome number by half, while meiosis II separates the sister chromatids.
Question 3: What is the role of crossing over during meiosis?
Answer: Crossing over is a process that exchanges genetic material between homologous chromosomes, resulting in genetic diversity among the resulting gametes.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of mitosis?
Mitosis plays a pivotal role in cell growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction, ensuring the production of genetically identical daughter cells.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in the production of four haploid daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, a process crucial for sexual reproduction.